Research
Drug discovery and mechanisms
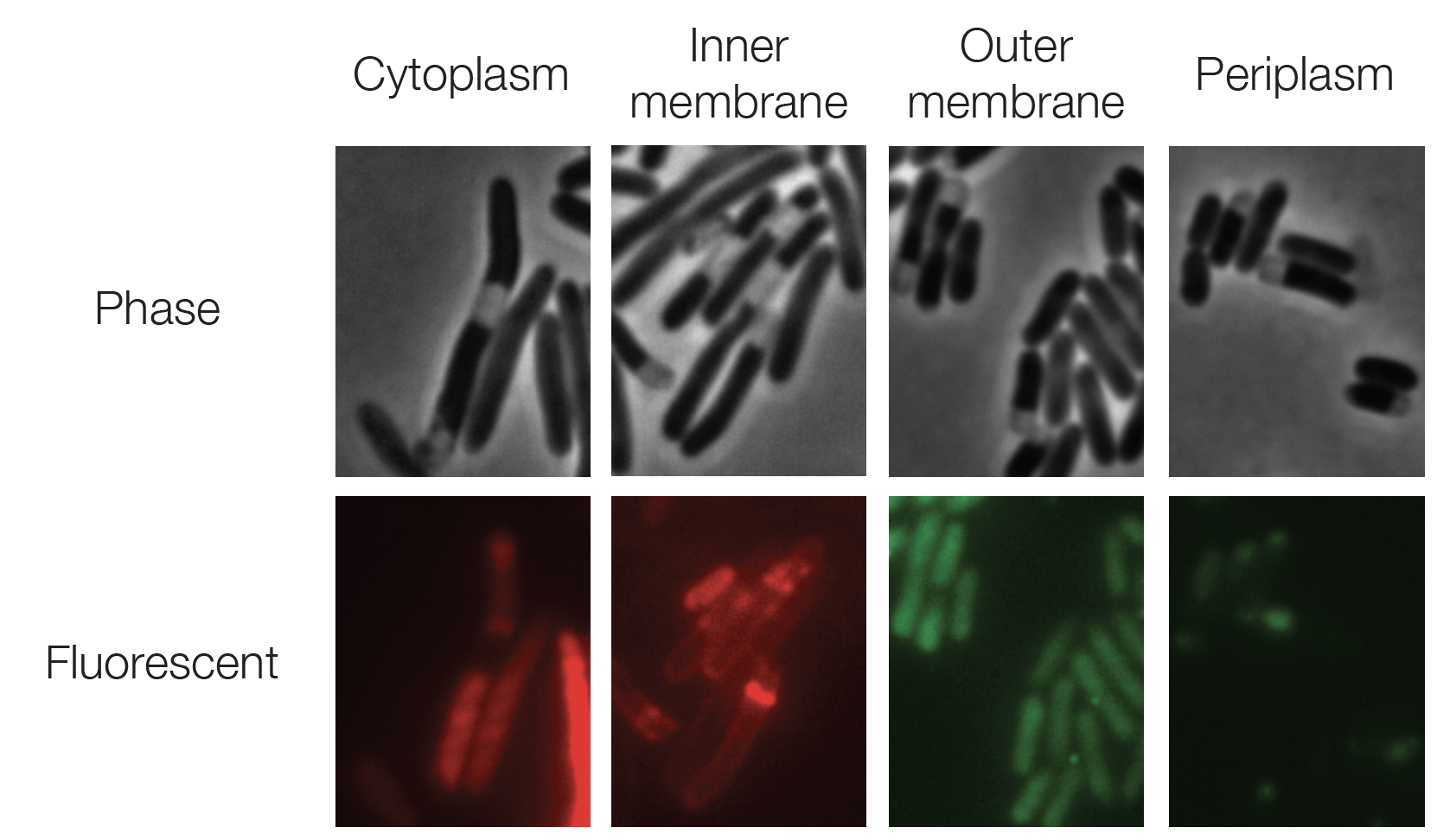
How can we develop the next great classes of drugs?
Understanding how drugs work and how to more efficiently discover them are two of the most important questions in biology. My research studies how drugs like antibiotics work and how to counter crises like antibiotic resistance, using tools from quantitative biophysics and single-cell biology. My collaborators and I are also using deep learning to discover novel drug classes.
Main collaborators: James J. Collins and Lars D. Renner
Relevant publications:- F. Wong*, E. J. Zheng*, J. A. Valeri, N. M. Donghia, M. N. Anahtar, S. Omori, A. Li, A. Cubillos-Ruiz, A. Krishnan, W. Jin, A. L. Manson, J. Friedrichs, R. Helbig, B. Hajian, D. K. Fiejtek, F. F. Wagner, H. H. Soutter, A. M. Earl, J. M. Stokes, L. D. Renner, and J. J. Collins, Discovery of a structural class of antibiotics with explainable deep learning, Nature (2023). PDF
- E. J. Zheng, J. A. Valeri, I. W. Andrews, A. Krishnan, P. Bandyopadhyay, M. N. Anahtar, A. Herneisen, F. Schulte, B. Linnehan, F. Wong, J. M. Stokes, L. D. Renner, S. Lourido, and J. J. Collins, Discovery of antibiotics that selectively kill metabolically dormant bacteria , Cell Chemical Biology (2023). PDF
- F. Wong, C. de la Fuente-Nunez, and J. J. Collins, Leveraging artificial intelligence in the fight against infectious diseases, Science 381, 164-170 (2023). PDF
-
F. Wong*, S. Omori*, N. M. Donghia, E. J. Zheng, and J. J. Collins, Discovering small-molecule senolytics with deep neural networks,
Nature Aging 3, 734-750 (2023). PDF
- F. Wong*, A. Krishnan*, E. J. Zheng, H. Stärk, A. L. Manson, A. M. Earl, T. Jaakkola, and J. J. Collins, Benchmarking AlphaFold-enabled molecular docking predictions for antibiotic discovery, Molecular Systems Biology 18, e11081 (2022). PDF
- F. Wong, J. M. Stokes, S. C. Bening, C. Vidoudez, S. A. Trauger, and J. J. Collins, Reactive metabolic byproducts contribute to antibiotic lethality under anaerobic conditions, Molecular Cell, 82, 3499-3512 (2022). PDF
- M. A. Lobritz*, I. W. Andrews*, D. Braff, C. B. M. Porter, A. Gutierrez, Y. Furuta, L. B. G. Cortes, T. Ferrante, S. C. Bening, F. Wong, C. Gruber, C. Bakerlee, G. Lambert, G. C. Walker, D. J. Dwyer, and J. J. Collins, Increased energy demand from anabolic-catabolic processes drives β-lactam antibiotic lethality, Cell Chemical Biology 29, 276-286 (2022). PDF
- F. Wong, J. M. Stokes, B. Cervantes, S. Penkov, J. Friedrichs, L. D. Renner, and J. J. Collins, Cytoplasmic condensation induced by membrane damage is associated with antibiotic lethality, Nature Communications 12, 2321 (2021). PDF
- F. Wong*, S. Wilson*, R. Helbig, S. Hegde, O. Aftenieva, H. Zheng, C. Liu, T. Pilizota, E. C. Garner, A. Amir, and L. D. Renner, Understanding beta-lactam-induced lysis at the single-cell level, Frontiers in Microbiology 12, 712007 (2021). PDF
- F. Wong and A. Amir, Mechanics and dynamics of bacterial cell lysis, Biophysical Journal 116, 2378-2389 (2019). PDF
Quantitative biophysics
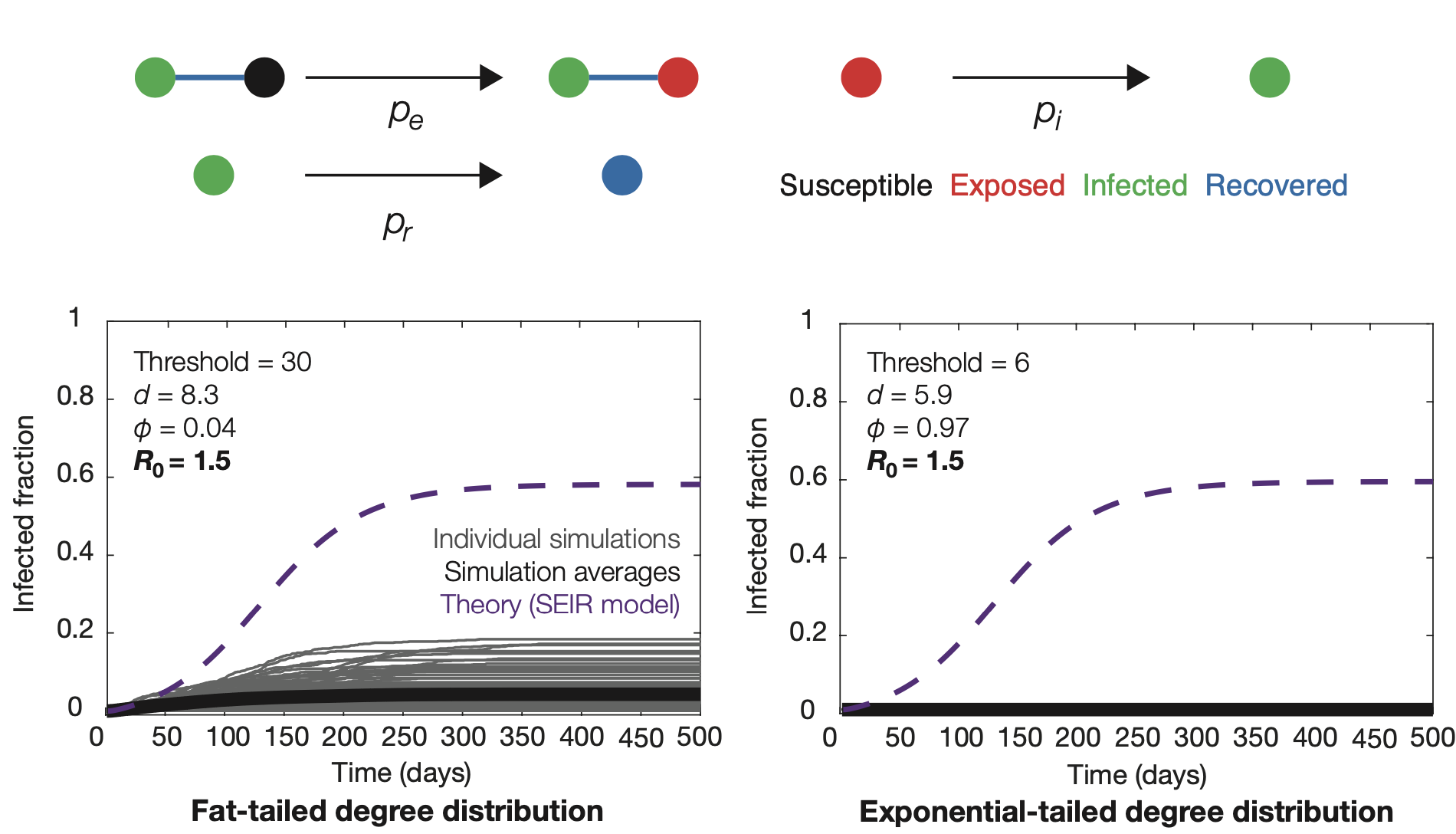
What physical and mathematical equations describe biological systems?
I am interested in all aspects of quantitative biophysics. My physical and mathematical modeling-based approaches to understanding these phenomena have shed light on processes as diverse as SARS-CoV-2 transmission and cellular morphogenesis.
Main collaborators: James J. Collins and Ariel Amir
Relevant publications:- F. Wong and J. J. Collins, Evidence that coronavirus superspreading is fat-tailed, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 117, 29416-29418 (2020). PDF
- F. Wong, E. C. Garner, and A. Amir, Mechanics and dynamics of translocating MreB filaments on curved membranes, eLife 8, e40472 (2019). PDF
- F. Wong and A. Amir, Mechanics and dynamics of bacterial cell lysis, Biophysical Journal 116, 2378-2389 (2019). PDF
- F. Wong*, L. D. Renner*, G. Özbaykal, J. Paulose, D. B. Weibel, S. van Teeffelen, and A. Amir, Mechanical strain sensing implicated in cell shape recovery in Escherichia coli, Nature Microbiology 2, 17115 (2017). PDF
Cell physiology and mechanics
How do bacteria regulate their physiology?
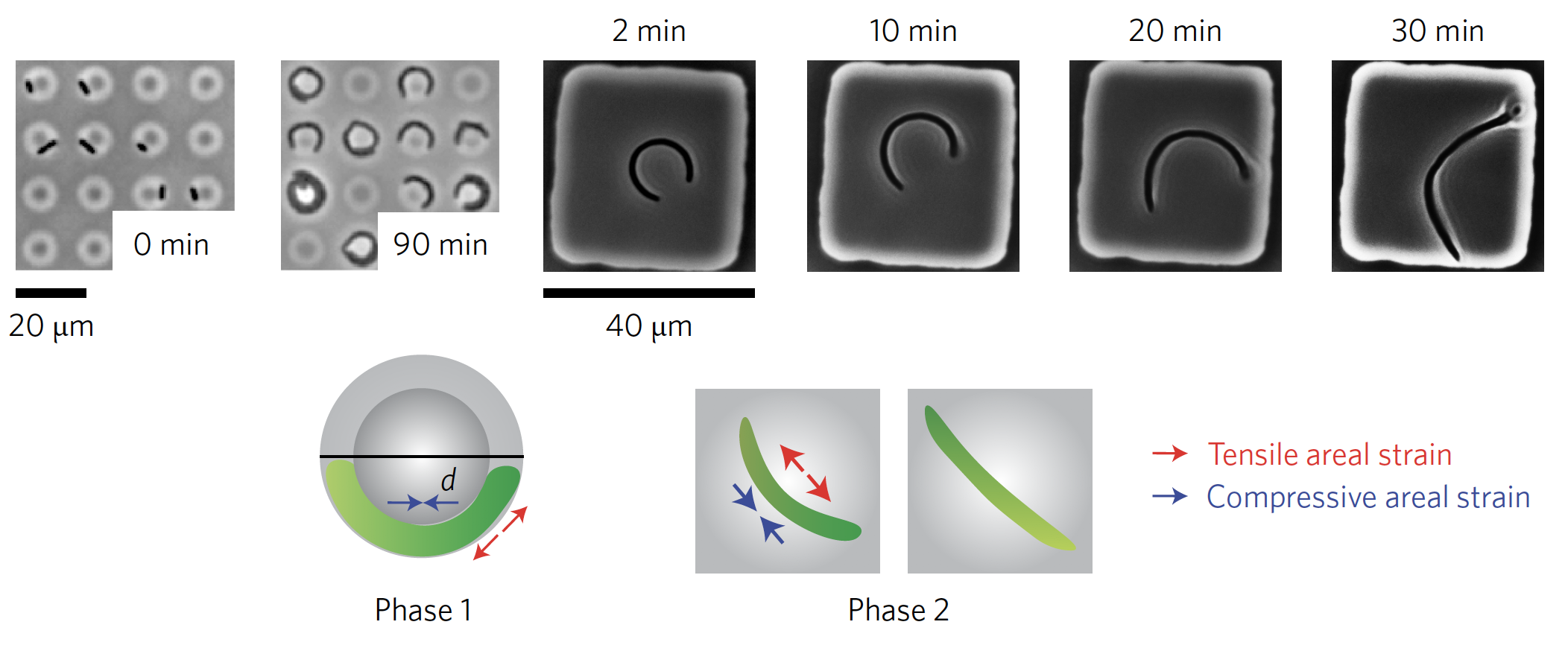
Cellular physiology is one of the pillars of modern biology; I study this using bacteria as a model system. For instance, many bacteria, including the rod-shaped Escherichia coli or the round Staphylococcus aureus, regulate their shapes during growth and in response to morphological perturbations with remarkable precision. My work has shown that bacterial cells generate their shapes in part by using biological pathways to sense mechanical cues.
Main collaborators: Ariel Amir, Lars D. Renner, Sven van Teeffelen, and Ethan C. Garner
Relevant publications:- F. Wong, E. C. Garner, and A. Amir, Mechanics and dynamics of translocating MreB filaments on curved membranes, eLife 8, e40472 (2019). PDF
- F. Wong and A. Amir, Mechanics and dynamics of bacterial cell lysis, Biophysical Journal 116, 2378-2389 (2019). PDF
- S. Hussain*, C. N. Wivagg*, P. Szwedziak, F. Wong, K. Schaefer, T. Izoré, L. D. Renner, M. J. Holmes, Y. Sun, A. W. Bisson-Filho, S. Walker, A. Amir, J. Löwe, and E. C. Garner, MreB filaments align along greatest principal membrane curvature to orient cell wall synthesis, eLife 7, e32471 (2018). PDF
- F. Wong*, L. D. Renner*, G. Özbaykal, J. Paulose, D. B. Weibel, S. van Teeffelen, and A. Amir, Mechanical strain sensing implicated in cell shape recovery in Escherichia coli, Nature Microbiology 2, 17115 (2017). PDF
Information processing in biology
How is information transmitted in cells, and how is energy being used in biological systems?
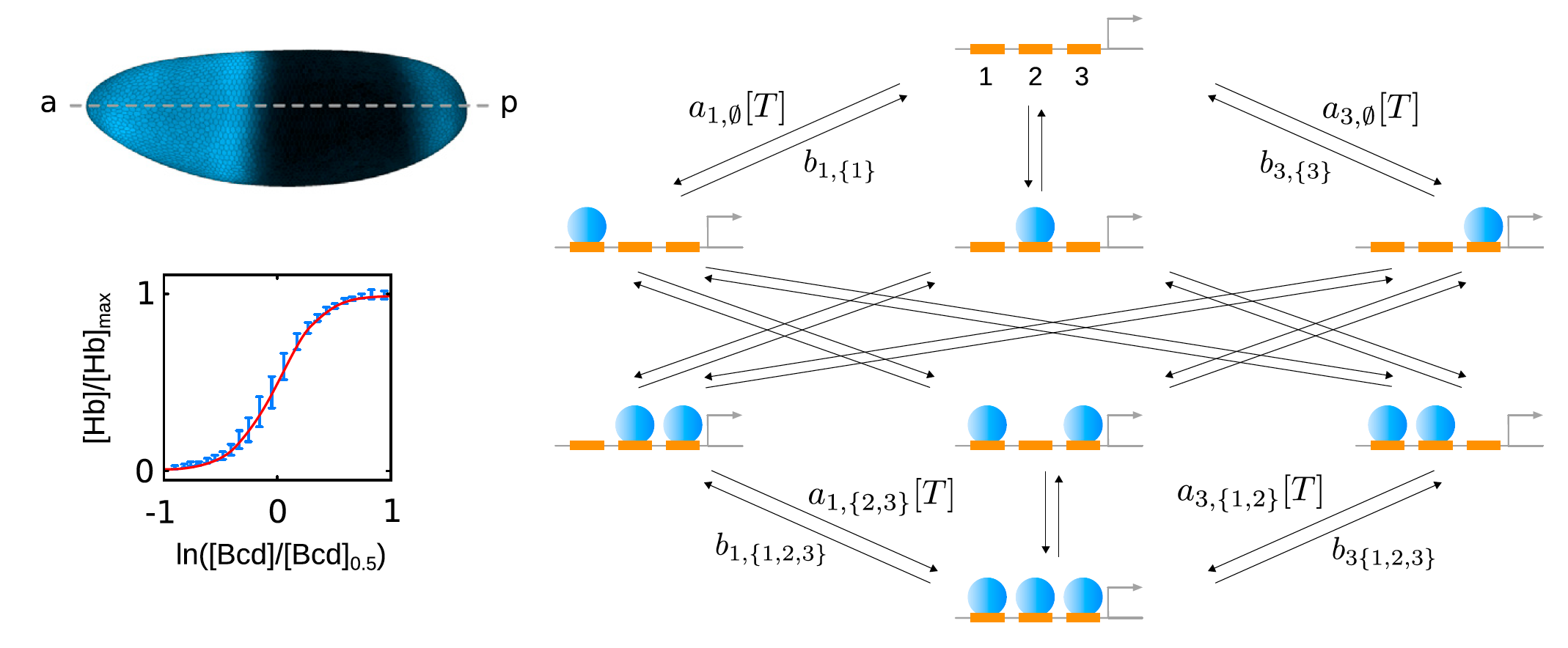
Many biological processes such as proofreading in DNA replication or eukaryotic gene regulation are complex: they exhibit dissipation or higher-order cooperativity between multiple molecular components. My work has elucidated how these different systems process information, as well as the role of energy expenditure in driving the biological circuits needed to sustain life.
Main collaborators: Jeremy Gunawardena, Angela DePace, and Debashish Chowdhury
Relevant publications:- J. Biddle,* R. Martinez-Corral,* F. Wong, and J. Gunawardena, Allosteric conformational ensembles have unlimited capacity for integrating information, eLife 10, e65498 (2021). PDF
- F. Wong and J. Gunawardena, Gene regulation in and out of equilibrium, Annual Reviews of Biophysics 49, 199-226 (2020). Full Text
- F. Wong, A. Dutta, D. Chowdhury, and J. Gunawardena, Structural conditions on complex networks for the Michaelis-Menten input-output response, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 115, 9738-9743 (2018). PDF
- F. Wong, A. Amir, and J. Gunawardena, Energy-speed-accuracy relation in complex networks for biological discrimination, Physical Review E 98, 012420 (2018). PDF
- J. Estrada, F. Wong, A. DePace, and J. Gunawardena, Information integration and energy expenditure in gene regulation, Cell 166, 234-244 (2016). PDF
- T. Ahsendorf*, F. Wong*, R. Eils, and J. Gunawardena, A framework for modelling gene regulation which accommodates non-equilibrium mechanisms, BMC Biology 12, 102 (2014). PDF