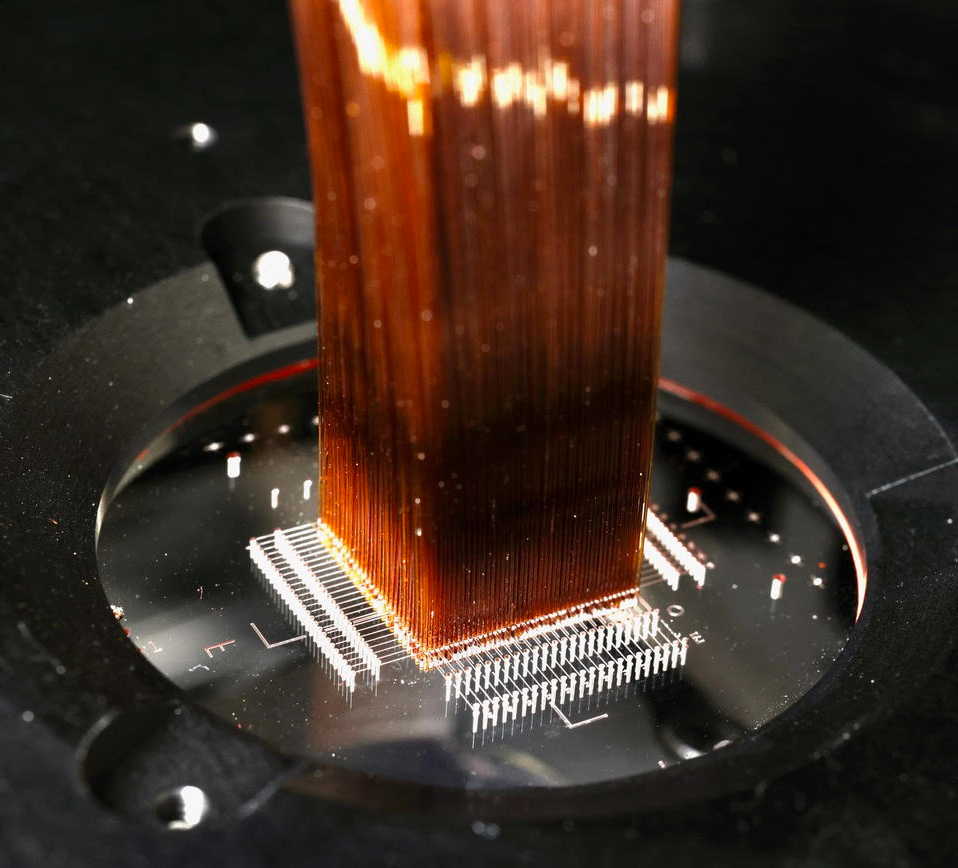
Fiber Plug Plate
Image of the LLAMAS integral Field Unit with fibers bonded into the plug plate. Each fiber is 120 microns in diameter, similar to a human hair, and the total active area of the IFU is approximately 12 x 12 mm
Technical Description and Instrument Characteristics
The Large Lenslet Array Magellan Spectrometer (LLAMAS) is a facility-class optical integral field unit (IFU) spectrograph under construction for the Magellan Telescopes. Offering 3D spectral images over the full optical band, LLAMAS will be the first wide-field IFU on a US telescope in the Southern Hemisphere.
Light at the telescope focus is sliced by a lithographic array of 2400 microscopic lenslets and fed into corresponding optical fibers. Each fiber subtends 0.75” on the sky, and illuminates the pseudo-slit of a R~2200 (average) spectrum. The fibers are grouped into eight identical spectrographs each of which has three chromatically optimized channels, imaged onto a set of 24 CCDs.
As a facility instrument, LLAMAS will be available for use by all Magellan consortium members, and also to the US community via allocation of nights competed by NOIRLab as part of our MSIP funding agreement. Although its use cases are very broad, the instrument's technical requirements were developed around three design reference programs: (a) redshift determination for galaxy clusters discovered by the South Pole Telescope, (b) observations of the circumgalactic medium in emission and absorption, and (c) rapid observation of transient events discovered by the Rubin Observatory.
| Specification | LLAMAS |
|---|---|
| Field of View | 35" x 34" |
| Spatial Sampling Pitch | 0.75" |
| IFU Sky Filling Factor | >93% |
| Number of Fibers | 2400 |
| Spectral Resolution (Blue channel) | R=1680-2750 (from 350-470nm, respectively) |
| Spectral Resolution (Green channel) | R=1500-2410 (470-692nm) |
| Spectral Resolution (Red channel) | R=2000-2750 (690-980nm) |
| Bandpass per exposure | 350-975 nm |
| Blue/Green Dichroic Crossover | 470 nm |
| Green/Red Dichroic Crossover | 692 nm |
The LLAMAS IFU consists of a litographically etched microlens array which projects images of the telescope pupil onto the face of 2400 corresponding A/R coated optical fibers. The fibers are bonded into a matching "plug plate" with 2400 lighographically etched precision holes.

Image of the LLAMAS integral Field Unit with fibers bonded into the plug plate. Each fiber is 120 microns in diameter, similar to a human hair, and the total active area of the IFU is approximately 12 x 12 mm
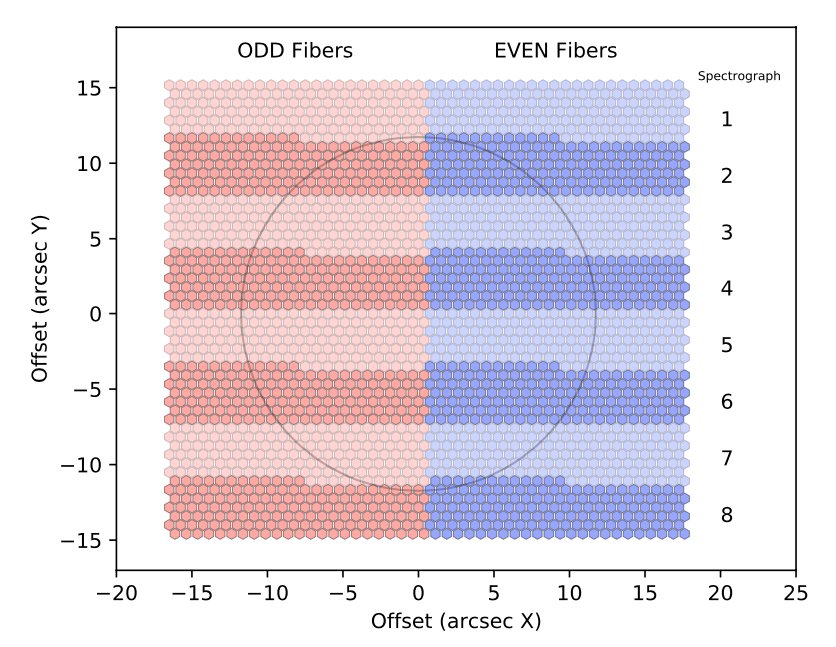
The IFU fibers map to pseudo slits of 8 identical spectrographs, seen in bands from top to bottom. Within each spectrograph, the left and right sides of the IFU map onto odd (1,3,5,7...) and even (0,2,4,6...) fiber numbers on the slit. With this mapping a user may occult half of the field to obtain spectra with twice the inter-trace separation for control of systematics. The circle indicates a sky area of R=100 pkpc at z=2.0
LLAMAS IFU fibers are multiplexed into a set of 8 functionally identical spectrographs, each of which has a 300-fiber pseudo-slit. Each spectrograph uses dichroics to split the specrum into blue, green, and red wavelength channels with matched VPH grisms, and optimized optics, coatings, and sensors. The blue and green CCDs are only optimized through A/R coatings, but the red channel CCDs are deep-depletion CCD42-40 models from e2v. With 8 spectrographs and 3 channels per spectrograph, LLAMAS required 24 custom-designed F/1 optical cameras, assembled and aligned at MIT. The layout resembles the DESI spectrographs in many ways, but is tuned slightly differently to match the fiber etendue to Magellan's expected sky backgrounds.
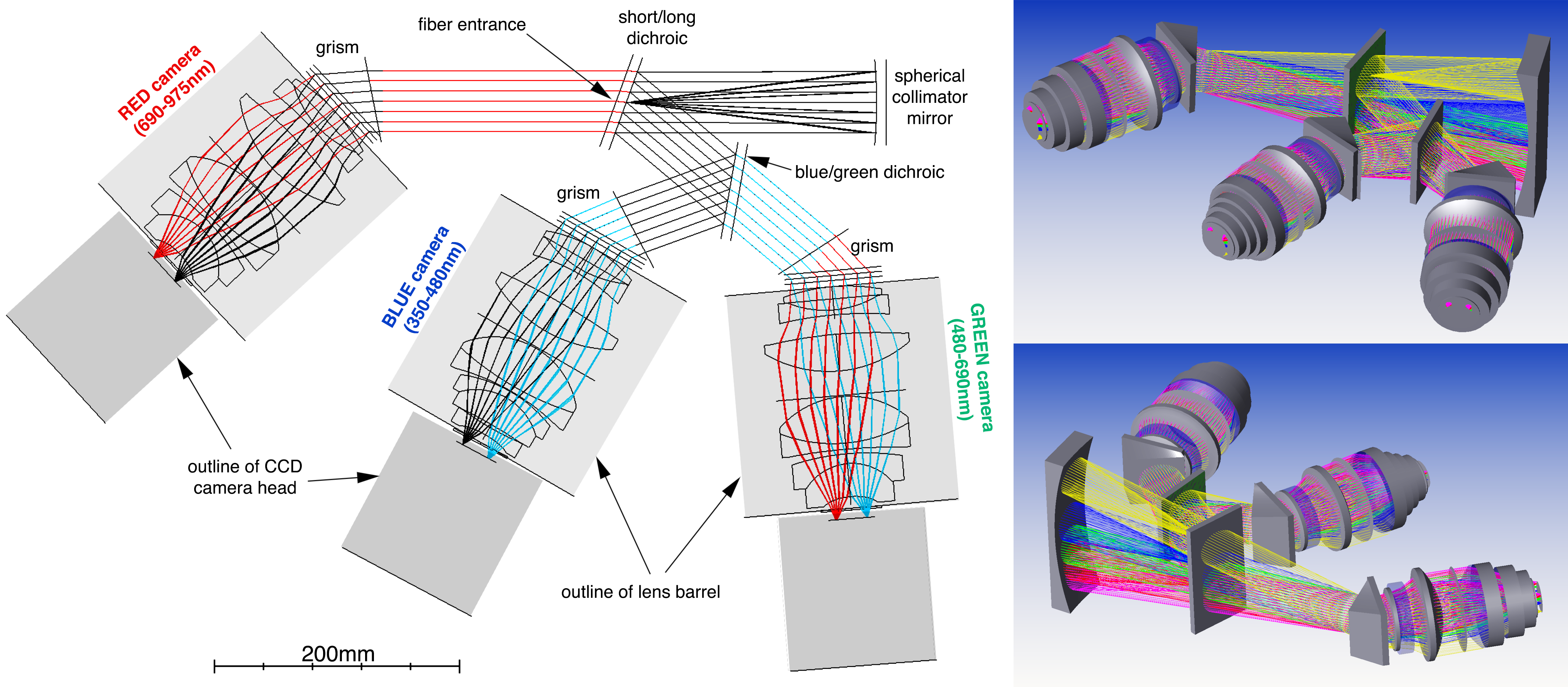
The fiber slit emerges in front of the blue camera, and directs output light to the collimator at upper right. The return beam is split by two dichroics into the the wavelength channels and dispersed by VPH grisms, one at the entrance pupil of each camera. The spectra are recorded on 2048x2048 pixel, thermo-electrically cooled CCDs manufactured by Raptor Photonics.
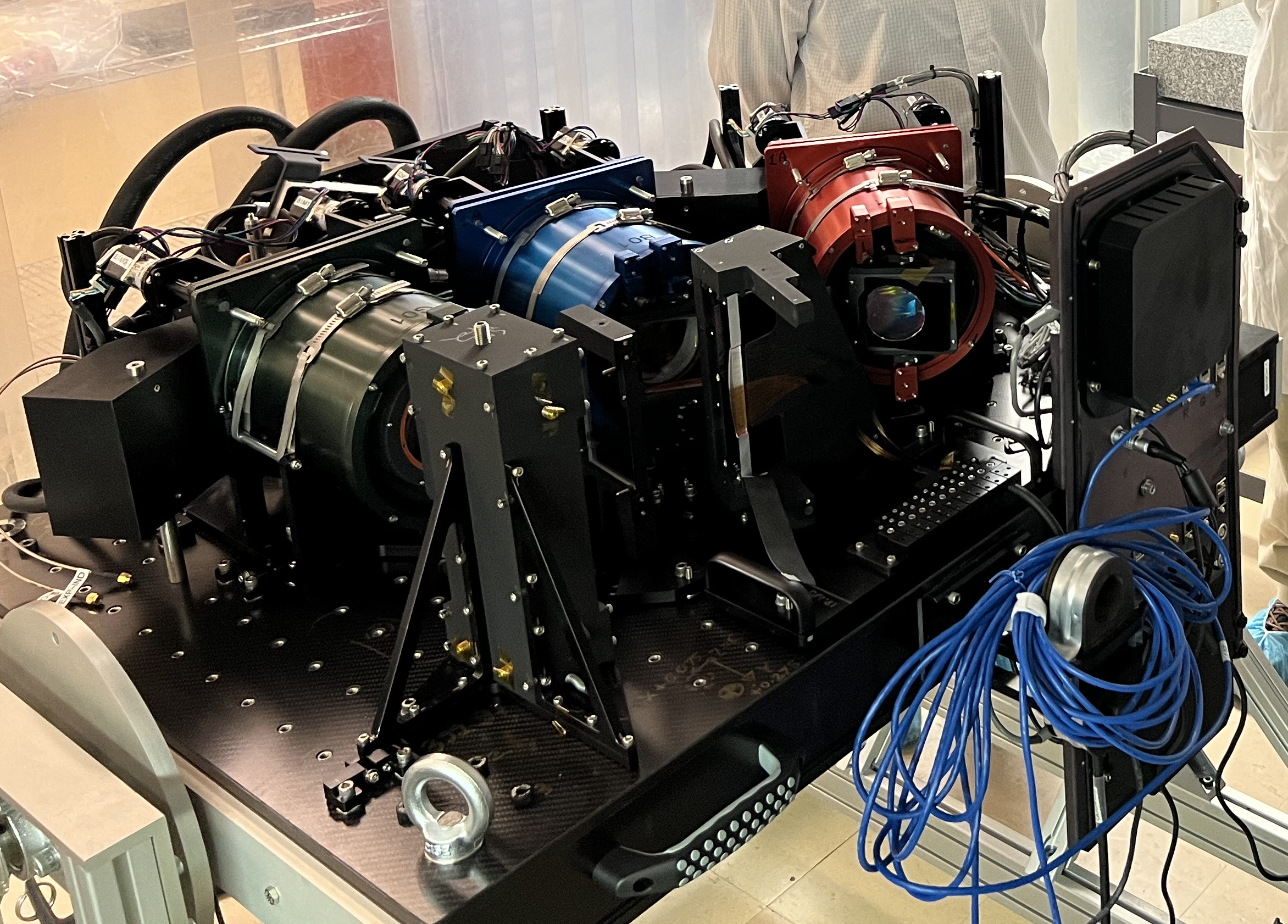
Photo of one spectrograph during asssembly/alignment. This assembly is a mirror image of the layout shown at left. This is because each carbon-fiber bench has two spectrographs: one on each face. The benches are oriented vertically during operation to symmetrize gravity loads.
The plot below shows the projected total throughput of the instrument, from the front of the IFU to the focal plane. This is taken from a roll-up of lab-measured as-built transmission and reflection of optical elements, lab-measured grating efficiencies and sensor QE, as well as estimates of vignetting and losses from focal-ratio degradation. It does not include telescope or atmosphere losses. Horizonal lines indicate design requirements on average %T (yellow) and wavelength-dependent %T (black).