




The following is a list of the overview information in this chapter.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
What Is Software Usage Monitoring page 265 What Can Software Usage Monitoring Do page 265 How Can Software Usage Monitoring Be Used page 266 How Software Usage Monitoring Works page 268 Before Using Software Usage Monitoring page 271 Generating Software Usage Report Entries page 275 Transferring Software Usage Entries on a Client to the Master Log File page 288 on the Software Usage Monitoring Server Printing Software Usage Data from the Master Log File page 291 Removing the Master Log File page 295 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following is a list of the step-by-step instructions in this chapter.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
How to Verify Software Usage Monitoring Has Been Installed on a page 271 Software Usage Monitoring Server How to Verify That Software Usage Monitoring Is Installed and Enabled page 272 on a Client How to Verify that Software Usage Monitoring is Enabled on a Host in a page 273 Shared File System Environment How to Stop the swu_svr Daemon page 274 How to Start the swu_svr Daemon page 274 How to Monitor Software Usage Using a Command-Line Interface page 275 How to Monitor Software Usage Using a Shell Script Wrapper page 279 How to Add Software Usage Monitoring to a Shell Script Program page 282 Executable Command Line How to Embed Software Usage Monitoring into Applications page 284 How to Transfer Software Usage Entries on the Client to the Master Log page 290 File on the Software Usage Monitoring Server How to Print Software Usage Data from the Master Log File page 294 How to Remove the Master Log File page 295 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Software usage monitoring is a compilation of software programs that enable you to monitor software usage in your computer system. The software usage monitoring system tracks the software usage and installations across network servers and workstations, to simplify system administration and purchasing decisions. For example, after using software usage monitoring, you may find that some software is never used while other software may be used repeatedly and needs additional licenses. In addition, you may find that a piece of software is installed on a workstation and is never used; this software could be used by another user who needs it.
The software usage monitoring system is not intended to be a licensing manager, nor does it track all software usage on your computer system. The software usage monitoring system functions as a push system rather than a pull system. That is, the software monitoring system cannot randomly obtain usage information from your computer system. Software running on your computer system must push usage information to the software usage monitoring server.
Software usage monitoring can do three basic tasks:
Software usage monitoring accomplishes these tasks using commands which are listed and described in Table 13-1.
Note - Refer to the man pages for detailed descriptions of the commands.
Table 13-1 Software Usage Monitoring Commands
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command Description ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
swu_rpt (command or function) Creates a software usage entry and places it into the
local queue (/var/opt/SUNWswusg/swusage) on the
client or the master log file on the software usage
monitoring server
(/var/opt/SUNWswusg/swusage.log)
swu_queue command Moves the software report entries in the local queue
(/var/opt/SUNWswusg/swusage) to the software
usage monitoring server; also enables and disables the
local queue
swu_svr command Software usage monitoring daemon which receives
software usage reports sent by the swu_queue
command from the client or by swu_rpt function
swu_print command Formats and prints usage information in the master log
file (/var/opt/SUNWswusg/swusage.log) to stdout
or another file
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To generate software usage entries, you must run the swu_rpt command or function with your software applications. You can accomplish this by using any of the following:
Note - The end record may not be accurate if the command returns after spawning a new process (for example, in the background).
Note - To use the embedded application method, you must have access to the application's source code.
How to implement these methods is described in detail in "Generating Software Usage Report Entries" on page 275.
The software usage monitoring system can be used in a client/server environment or in a shared file system environment. Software usage monitoring operates differently, depending upon which environment it is run. The following sections describe how software usage monitoring operates in each environment.
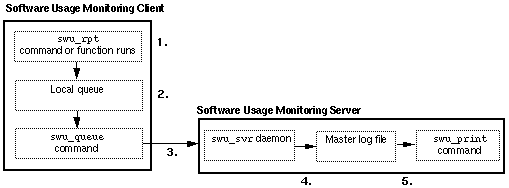
Figure 13-1 shows an illustration of the software usage monitoring sequence of events when used in a client/server environment.
Note - The client may also act as a software usage server in that it may have the swu_svr daemon, master log file, and swu_print command installed on the client.
The following list describes the sequence of events.
Note - If the local queue has been disabled, no report entries will be logged.
Note - Files can be transferred manually by a root user from the local queue to the swu_svr daemon using the swu_queue command using the -F option.
Note - If the swu_svr daemon is not running on the software usage monitoring server specified in the entry, that entry in the local queue is removed from the queue.
Note - This sequence of events shows the order in which commands are run; however, you should note that the swu_rpt command or function could be run numerous times before the swu_queue command transfers software usage report entries from the local queue.
Software usage monitoring operates in a similar manner in a shared file system environment as it does in a client/server environment. By installing software usage monitoring on a dedicated software usage monitoring server, you can share the binary files with other hosts in your network.
Figure 13-2 shows an illustration of the software usage monitoring sequence of events when used in a shared file system environment.
The following list describes the sequence of events.
Note - If the swu_svr daemon is not running on the host server, the entry is lost.
Before you use software usage monitoring, you need to complete a number of steps. Usually, these steps only need to be done once; however, it may be necessary to repeat some of them.
The steps required to set up software usage monitoring depend upon the environment in which you intend to run software usage monitoring. The following procedures describe how to set up software usage monitoring on a server and/or a client if you so choose.
--------------------------
$ cd /opt/SUNWswusg/bin $ ls swu_print swu_svr --------------------------
If software usage monitoring has not been installed, refer to the Solstice AdminSuite 2.3 Installation and Product Notes for information about installing software usage monitoring.
-------------------------------------------------------------
$ ps -ef | /usr/bin/grep swu_svr root 264 1 0 Jan 04 console 2:43 /opt/SUNWswusg/bin/swu_svr jod 752 311 1 14:50:16 pts/3 0:00 grep swu_svr $ -------------------------------------------------------------
If the swu_svr daemon is not running, start the swu_svr daemon. Refer to the "Starting and Stopping the swu_svr Daemon" on page 274 that describes how to start and stop the swu_svr daemon.
Note - If you wish to generate software usage monitoring information on a host, the software usage monitoring client binary packages should be installed on that host or should be made available to that host through NFS.
--------------------------
$ cd /opt/SUNWswusg/bin $ ls swu_queue swu_rpt --------------------------
If software usage monitoring has not been installed, refer to the Solstice AdminSuite 2.3 Installation and Product Notes for information about installing software usage monitoring.
----------------------------------
$ cd /var/opt/SUNWswusg/swusage $ ls $ ----------------------------------
If queue_disabled appears after the ls command, login as root and enable the queue as shown below.
------------------------------------
$ ls queue_disabled # /opt/SUNWswusg/bin/swu_queue -e # ls # ------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
$ rpcinfo -t host 120100 program 120100 version 1 ready and waiting --------------------------------------------
Note - Refer to the Solstice AdminSuite 2.3 Installation and Product Notes document for information about how to set up your swusage_host server.
When software usage monitoring is installed, the swu_svr daemon is started on the software usage monitoring server. At times, you may want to stop or restart the swu_svr daemon. The following procedures describe how to start and stop this daemon.
------------------------------
# /etc/init.d/swusage start ------------------------------
-----------------------------
# /etc/init.d/swusage stop -----------------------------
Software usage monitoring report entries can be generated using the following methods:
Each method uses the same basic software usage components; however, the methods access the components differently. The following sections describe each method and the procedures used to implement each method.
The command-line interface method is probably the simplest method of implementing software usage monitoring; however, it can also be the most taxing method as it requires you to manually type in each command each time you run software usage monitoring with an application.
At the shell prompt, generate a usage report using one of the following swu_rpt command lines.
To create a software usage report entry specifying that the associated program has been installed, use the -i option.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
$ swu_rpt -p product-name [-I identifier] [-s server] [-a attr1=val1, attr2=val2,...] -i ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To create a software usage report entry specifying that the associated program has started, use the -b option.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
$ swu_rpt -p product-name [-I identifier] [-s server] [-a attr1=val1, attr2=val2,...] -b -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To create a software usage report entry specifying that the associated program has ended, use the -e option.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
$ swu_rpt -p product-name [-I identifier] [-s server] [-a attr1=val1, attr2=val2,...] -e -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To create software usage report entries specifying a begin and an end entry for the associated program, use the -c option.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
$ swu_rpt -p product-name [-I identifier] [-s server] [-a attr1=val1, attr2=val2,...] -c command ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In these commands,
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
-p product-name Indicates the name of the product that software usage is being recorded for; this option must be included. -I identifier Specifies a numerical identifier for usage records; swu_rpt will provide its own identifier if one is not specified. -s server Specifies the software usage monitoring server to which the usage records are to be sent. The default is the host aliased to swusage_host. -a attr1=val1, Allows the user to give the software usage entry attr2=val2,... unique or more descriptive information. -b Indicates that a begin entry will be recorded. -e Indicates that an end entry will be recorded. -i Indicates that an install entry will be recorded. -c command Indicates that the command or program listed after the -c option should be executed and that a begin and end entry should be recorded. -----------------------------------------------------------------------
The following example shows the software usage monitoring command as used from a command line, which starts the FrameMaker program using the command maker, and logs the application using the software usage monitoring swu_rpt command.
--------------------------------------------------------
$ swu_rpt -p FrameMaker -I 29581 -s sherlock -c maker --------------------------------------------------------
In this example, two software usage report entries are created because the -c option was used (the -c option creates a begin and an end entry). The entries look like the following.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Report Entry 1 Report Entry 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------
Type Admin/Usage Type Admin/Usage
Product FrameMaker Product FrameMaker
SubType Begin SubType End
Time 8444845890 Time 8444845957
UserID 30581 UserID 30581
User jod User jod
Host buck Host buck
Domain forest.field.com Domain forest.field.com
HostID 1234567890 HostID 1234567890
Locale C Locale C
Version 1 Version 1
Ussage Server sherlock Usage Server sherlock
RecordID 29581 RecordID 29581
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Another method of monitoring software usage is to create a shell script that initiates a program. This method enables you to create a log entry each time a user executes the shell script. A shell script can be modified using one of two methods: you can create a shell script wrapper, or you can modify the script of an existing shell script program. Either method creates a begin and end software usage monitoring log entry.
Note - Using the shell script wrapper method may not be the best option if your command runs in the background. An end record is generated immediately after the command is executed and the time used is not accurate.
The following procedures describe how to implement each software usage monitoring shell script method.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
swu_rpt -p product name [-I identifier] [-s server] [-a attr1=val1, attr2=val2,...] -b -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In this command,
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
-p product-name Indicates the name of the product that software usage is being recorded for; this option must always be included. -I identifier Specifies a unique, alpha numeric identifier for usage records; swu_rpt will provide its own identifier if one is not specified. -s server Specifies the server to which the usage records are to be sent. The default is the host aliased to swusage_host. -a attr1=val1, Allows the user to give the software usage entry attr2=val2,... unique or more descriptive information. -b Indicates that a begin entry should be recorded. -----------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
swu_rpt -p product-name [-I identifier] [-s server] [-a attr1=val1, attr2=val2,...] -e -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In this command,
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
-p product-name Indicates the name of the product that software usage is being recorded for; this option must always be included. -I identifier Specifies a unique, numerical identifier for usage records; swu_rpt will provide its own identifier if one is not specified. -s server Specifies the server to which the usage records are to be sent. The default is the host aliased to swusage_host. -a attr1=val1, Allows the user to give the software usage entry attr2=val2,... unique or more descriptive information. -e Indicates that an end entry should be recorded. -------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following example shows the software usage monitoring commands added to a shell script called dir_script that lists the directory in which it was called, the files in the directory, and the current date and time.
----------------------------------------------------------
swu_rpt -p dir_script -I 295833 -s sherlock -a \ "Command1=pwd,Command2=ls,Options=-la,Command3=date" -b pwd ls -la date swu_rpt -p dir_script -I 295833 -s sherlock -a \ "Command1=pwd,Command2=ls,Command3=date" -e ----------------------------------------------------------
In this example, two software usage report entries are created and look like the following.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Report Entry 1 Report Entry 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------
Type Admin/Usage Type Admin/Usage
Product dir_script Product dir_script
SubType begin SubType end
Time 8444845890 Time 8444845892
UserID 30581 UserID 30581
User jod User jod
Host buck Host buck
Domain forest.field.com Domain forest.field.com
HostID 1234567890 HostID 1234567890
Locale C Locale C
Version 1 Version 1
Usage Server sherlock Usage Server sherlock
RecordID 295833 RecordID 295833
C_Command1 pwd C_Command1 pwd
C_Command2 ls C_Command2 ls
C_Options -la C_Command3 date
C_Command3 date
-----------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
swu_rpt -p product-name [-I identifier] [-s server] [-a attr1=val1, attr2=val2,...] -c command ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In this command,
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
-p product-name Indicates the name of the product that software usage is being recorded for; this option must always be included. -I identifier Specifies a unique, numerical identifier for usage records; swu_rpt will provide its own identifier if one is not specified. -s server Specifies the server to which the usage records are to be sent. The default is the host aliased to swusage_host. -a attr1=val1, Allows the user to give the software usage entry attr2=val2,... unique or more descriptive information. -c command Specifies the program executable command. -------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following example shows the software usage monitoring command added to a program executable command line that executes FrameMaker.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
swu_rpt -p Frame -I 295836 -s sherlock -a "Command=maker,Version=4.0" -c maker --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In this example, the software usage report entry looks like this:
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Report Entry 1 Report Entry 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------
Type Admin/Usage Type Admin/Usage
Product Frame Product Frame
SubType Begin SubType End
Time 8148244876 Time 8148244920
UserID 30581 UserID 30581
User jod User jod
Host buck Host buck
Domain forest.field.com Domain forest.field.com
HostID 1234567890 HostID 1234567890
Locale C Locale C
Version 1 Version 1
Usage Server sherlock Usage Server sherlock
RecordID 295836 RecordID 295836
C_Command maker C_Command maker
C_Version 4.0 C_Version 4.0
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Software usage monitoring can be implemented by embedding calls to the swu_rpt function into an application. This method works well for monitoring applications that you or others on your computer network have created.
For example, you may have created an online timecard to keep track of time spent on projects; however, you are not sure that it is being used by everyone. Within the online timecard application, you can embed calls to the swu_rpt function, which then generates usage reports every time the application is executed.
The following procedure provides information about how to embed the software usage monitoring report function within an application.
------------------------
#include <swusage.h'> ------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
swu_rpt ("Server_name", "Identifier", SWU_BEGIN, "Product name", avl) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
swu_rpt ("Server_name", "Identifier", SWU_END, "Product name", avl) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For static linking of the libraries:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
$ ... -I/opt/SUNWswusg/include -L/opt/SUNWswusg/lib -Bstatic -lswusage -lnsl ... ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For dynamic linking of the libraries:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
$ ... -I/opt/SUNWswusg/include -R/opt/SUNWswusg/lib -L/opt/SUNWswusg/lib -lswusage -lnsl ... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following example shows an application that includes the software usage monitoring function.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <stdio.h'> /* definition of NULL */ #include <swusage.h'> /* swu_rpt() prototype, swusage_alist definition */ #define ATTRIBUTE_COUNT 3 main() { struct swusage_alist avl[ATTRIBUTE_COUNT]; /* * Define some product specific attribute-value pairs that will * be included in the software usage report records. */ avl[0].u_attr = "ATTR_1"; avl[0].u_value = "val_1"; avl[1].u_attr = "ATTR_2"; avl[1].u_value = "val_2"; /* * Terminate the attribute list */ avl[2].u_attr = NULL; avl[2].u_value = NULL; /* * Create a begin record for the application */ swu_rpt("Server_name", "Identifier", SWU_BEGIN, "My product name", avl); /* * The application code would go here. */ /* * Create an end record for the application */ swu_rpt("Server_name", "Identifier",SWU_END, "My product name", avl); } ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
In this example, the software usage report entry looks like this:
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Report Entry 1 Report Entry 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------
Type Admin/Usage Type Admin/Usage
Product My product name Product My product name
SubType Begin SubType End
Time 8148244876 Time 8148244920
UserID 30581 UserID 30581
User jod User jod
Host buck Host buck
Domain forest.field.com Domain forest.field.com
HostID 1234567890 HostID 1234567890
Locale C Locale C
Version 1 Version 1
Usage Server Server_name Usage Server Server_name
RecordID Identifier RecordID Identifier
C_ATTR_1 val_1 C_ATTR_1 val_1
C_ATTR_2 val_2 C_ATTR_2 val_2
-----------------------------------------------------------------
If software usage monitoring is installed on a client and software usage entries have been recorded on the client, you need to transfer the software usage report entries in the client's local queue to the master log file on the software usage monitoring server. Figure 13-3 provides an illustration of where the data is located.
Figure 13-3 Software Usage Monitoring Files and Locations
The software usage report entries in the local queue are located in the /var/opt/SUNWswusg/swusage directory. The report entries are designated by an alphanumeric string. For example, if you entered the ls command in the local queue, you would see something like the following:
----------------------------------------------------------------
$ cd /var/opt/SUNWswusg/swusage $ ls swrepAAAa000Tv swrepAAAa000UL swrepBAAa000Tv swrepBAAa000UL ----------------------------------------------------------------
The software usage report entries are moved from this directory using the swu_queue command.
When the software usage monitoring system was installed, a cron job was added to the host's root crontab. This cron job runs the swu_queue command at a random time between midnight and 7 a.m. This swu_queue command transfers (flushes) the usage reports from the local queue to the master log file (/var/opt/SUNWswusg/swusage.log) on the software usage server specified in the usage entry.
Although this job runs automatically, there may be times when you wish to transfer the data in the local queue to the software usage monitoring server at a time other than when the cron job transfers the data. To do so, see "How to Transfer Software Usage Entries on the Client to the Master Log File on the Software Usage Monitoring Server" on page 290.
Note - When the swu_queue command is executed and the files are successfully transferred from the local queue to the master log file, the files are removed from the local queue; if the files do not get transferred (for example, the host specified in the entry was not running), the files in the local queue are not removed, which may cause your file system to fill. To prevent this from happening, you can disable the queue using the swu_queue -d command, which prevents usage records from being logged.
The following list explains what may happen when transferring software usage entries on the client to the master log file.
-------------------
# swu_queue -F -------------------
In this command,
--------------------------------------------------------
-F Transfers data in the local queue to the swu_svr daemon on the usage monitoring server. --------------------------------------------------------
After the software usage data has been moved from the local queue to the master log file on the host server, you may want to print the information in the master log file to another file, stdout (screen), or printer.
The software usage record entries are not formatted in the master log file. The swu_print command moves and formats the software usage report entries in the master log file to another file or the standard output device. Three options can be used with the swu_print command to format the entries differently.
The options available with the swu_print command are listed in Table 13-2, along with an example of how the software usage report entries are formatted with the associated option.
Table 13-2 swu_print Options
----------------------------------------------------------------
Option Format Example ----------------------------------------------------------------
-a PRODUCT SUBTYPE TIME RECORD_ID USER HOST
maker Begin Feb 26 17:08:17 IDstring jod sherlock
vi Begin Feb 27 19:09:19 IDstring jad holmes
-d TYPE=Admin/Usage
Product=maker
SubType=Begin
Time=819653293
UserID=49740
User=jod
Host=buck
Domain=field.forest.com
HostID=55003efc
Locale=C
Version=1
Server=sherlock
RecordID=IDstring
-s PRODUCT TIME USER HOST
maker 01:31:47 jod buck
vi 19:09:19 jad doe
----------------------------------------------------------------
Formatting these entries enables you to use awk or another search tool to search on keywords; formatting also enables you to easily translate the entries into another database or report.
Note - swu_print does not delete the software usage report entries from the master log file. In order to get rid of these entries, you must delete the master log file. Otherwise, entries are appended to the software usage report entries that you already copied out using the swu_print command. This could result in your file system becoming full; see "How to Remove the Master Log File" on page 295 for information about how to safely remove this file.
The report entries created by the software usage monitoring system vary depending upon the command used to generate the entry; however, all entries have some fields that will always appear. Table 13-3 provides a list of all possible report entries, along with a description of each entry, and a list of when the entry is used.
Table 13-3 Report Entries
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Field Possible Entries Description When Used -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Type Admin/Usage Indicates the record is a system administration, Always
software usage entry.
Product Varies Indicates the product name (or program name) of the Always
software that is being logged; specified with the
swu_rpt command or function.
User Varies Indicates the user who ran the software. The entry will Always
indicate the user's login name.
SubType Begin Intended to indicate that the software associated with swu_rpt command
this record has begun execution at the indicated time. options -b or -c
End Intended to Indicate that the software associated with swu_rpt command
this record has ended execution at the indicated time. options -e or -c
Install Intended to indicate that the software associated with swu_rpt command-i
this record has been installed. option
Enable Queue Indicates that the local swu_queue has been enabled. swu_queue command
-e option
Disable Queue Indicates that the local swu_queue has been disabled. swu_queue command
-d option
Time Varies Indicates the time the software began execution, ended Always
execution, or was installed. The value indicates the
value of time in seconds since 00:00:00 UTC January 1,
1970.
UserID Varies Indicates the user ID of the user who ran the software. Always
Host Varies Indicates the name of the workstation or server that the Always
program or command was run on.
Domain Varies Indicates the name service domain that the host resides Always
in.
HostID Varies Indicates the hardware serial number of the host Always
workstation or server.
Locale Varies Indicates the current value of the LANG environment Always
variable.
Version Varies Indicates the software usage monitoring version Always
(specified by the software usage monitoring program).
Usage Varies Indicates the software usage server to which usage Always
Server entries are to be sent.
RecordID Varies Indicates a unique, numerical ID that is specified with Always
the swu_rpt command; if no identifier is specified, the
parent process ID process and time is used as the
default.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note - If the field variable is not set, ?? would be the entry for the field variable because software usage monitoring could not determine its value.
To copy and format the software usage monitoring report entries in the master log file to another file or the standard output device, you need to perform the following procedure.
-------------------------------------------------------------
$ swu_print [-a|-d|-s] [-f filename] [-l log_file] -------------------------------------------------------------
In this command,
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
-a Specifies the format swu_print is to use (default - all). Refer to Table 13-2 for format examples. -d Specifies the format swu_print is to use (dump). Refer to Table 13-2 for format examples. -s Specifies the format swu_print is to use (summary). Refer to Table 13-2 for format examples. -f filename Specifies the file to which information in the log file will be directed. -l log_file Specifies the master log file. If this option is not specified, the default file /opt/SUNWswusg/swusage.log is used. -----------------------------------------------------------------------
To keep your file system from filling up, you will periodically have to clean up the master log file; however, you must follow a certain procedure to properly remove this log file to prevent future data loss.
The following procedure describes how to safely remove the master log file.
---------------------------------------------------
# mv /var/opt/SUNWswusg/swusage.log /tmp/tmp.log ---------------------------------------------------
--------------------
# rm /tmp/tmp.log --------------------
Note - This procedure moves all the software usage record entries located in swusage.log to a new file; any new records generated during this procedure will cause a new swusage.log file to be created.




