Black-body radiation
In physics, a black body is an idealized body which absorbs all radiation and emits radiation in a spectrum determined by its temperature. Planets and stars (including the earth and sun) can be approximated as black bodies. The intensity of radiation emitted by the black body is related to its temperature by the equation:
Where is the emissivity and is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant. An ideal black body has emissivity .
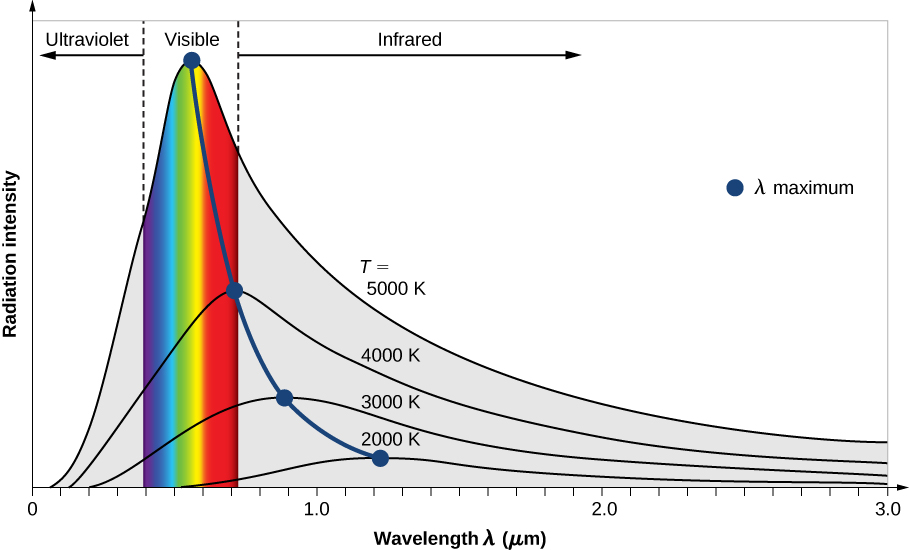
The wavelength emitted varies with the temperature as well. The graph below shows the wavelength and intensity of radiation emitted by a black body at different temperatures.