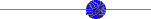 |
the JOINT SAMPLE SPACE:
Any experimental outcome can be fully described by ( Y, 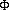 ), where ), where
Y = distance from the center of the pencil to the closest line (0 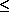 y y  d / 2), and d / 2), and
 = angle of the needle from the horizontal line (0 = angle of the needle from the horizontal line (0     ). ).
Since we know that the pencil was randomly thrown, this means that:
fY(y) = 2 / d , 0  y y  d / 2
f d / 2
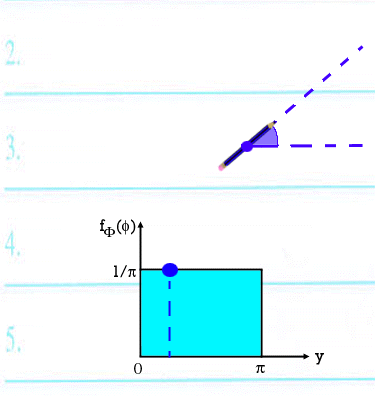
f ( ( ) = 1 / ) = 1 /  , 0 , 0    
Assuming independence, the joint distribution is:
fY, (y, (y, ) = 2 / ( ) = 2 / ( d ), d ),
0  y y  d / 2, 0 d / 2, 0    
... on to the Questions
|